We use phasor analysis.
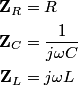 The total impedance is then 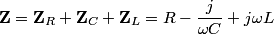 The phasor voltage is 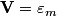 Therefore, the steady state phasor current is 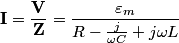 The magnitude of the phasor current (which equals the amplitude of the sinusoidal current) is 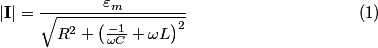 From equation (\ref{eqn81:1}), we see that the amplitude of the current is maximized when 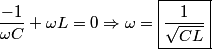 Therefore, answer (C) is correct. |